Tools¶
Emails sent¶
Users can have a look at the list of the automatic emails sent.
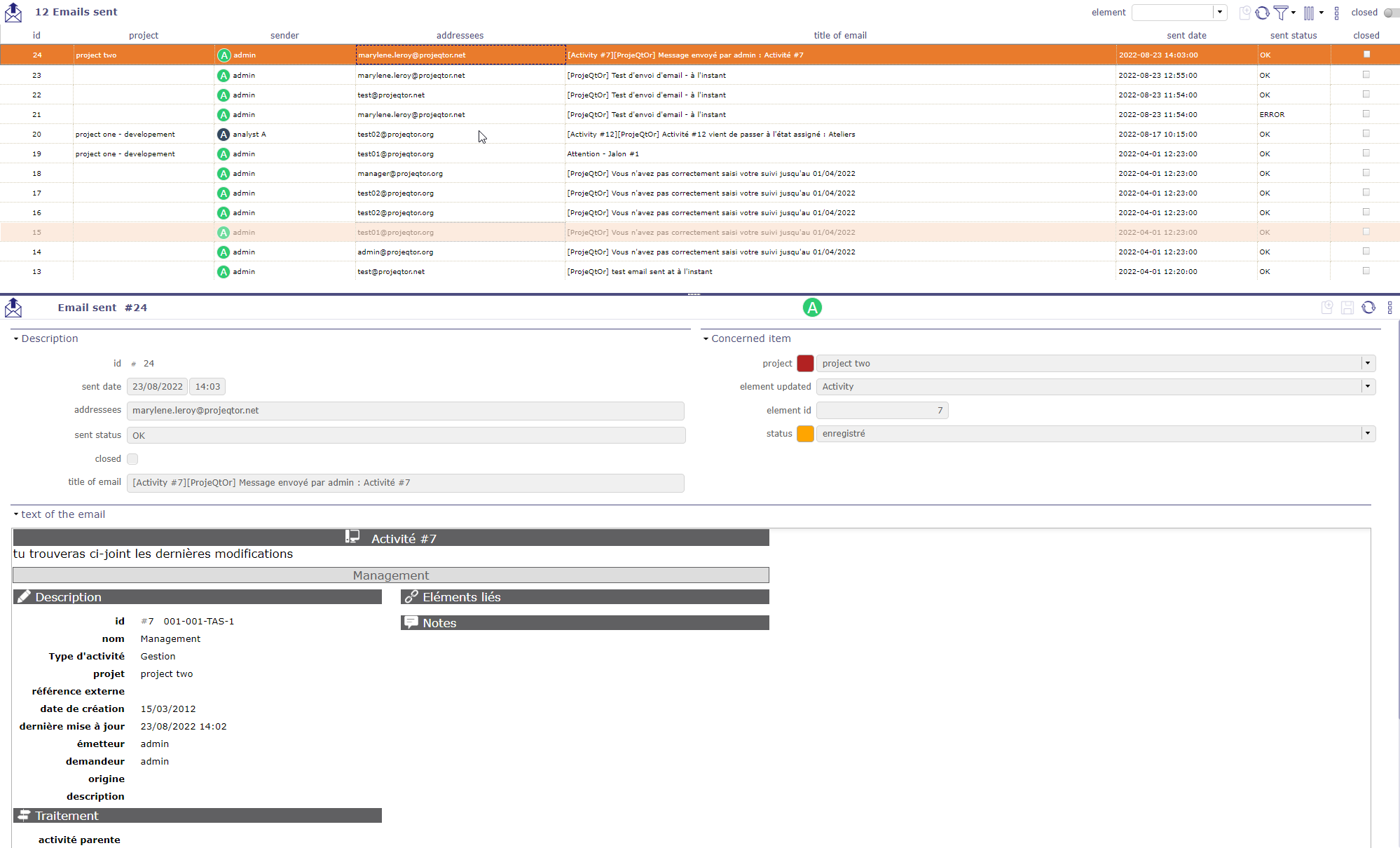
emails sent screen¶
All the information about the email, including the status showing whether the email was correctly sent or not.
You can see in the activity feed of the item the trace of the sending of the corresponding email with the subject and the text of the message.
Emails to send¶
You must enable the Activate email grouping option in the global parameters
The programmed emails will be grouped in this screen before their automatic sending based on the period entered in the global parameters
Scheduled report¶
In reports, you can schedule sending emails for accurate reports.
You can get the list and details of this programming on this screen
Click on Button ![]() to cancelled the programmation
to cancelled the programmation
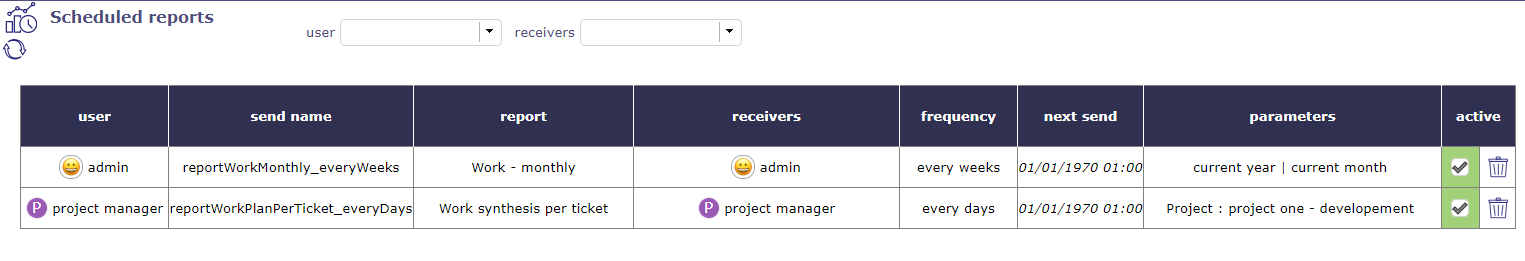
Scheduled report screen¶
See also
Alerts¶
Users can have a look at the alerts sent.
By default, administrators can see all the alerts sent, and other users only see their own alerts.
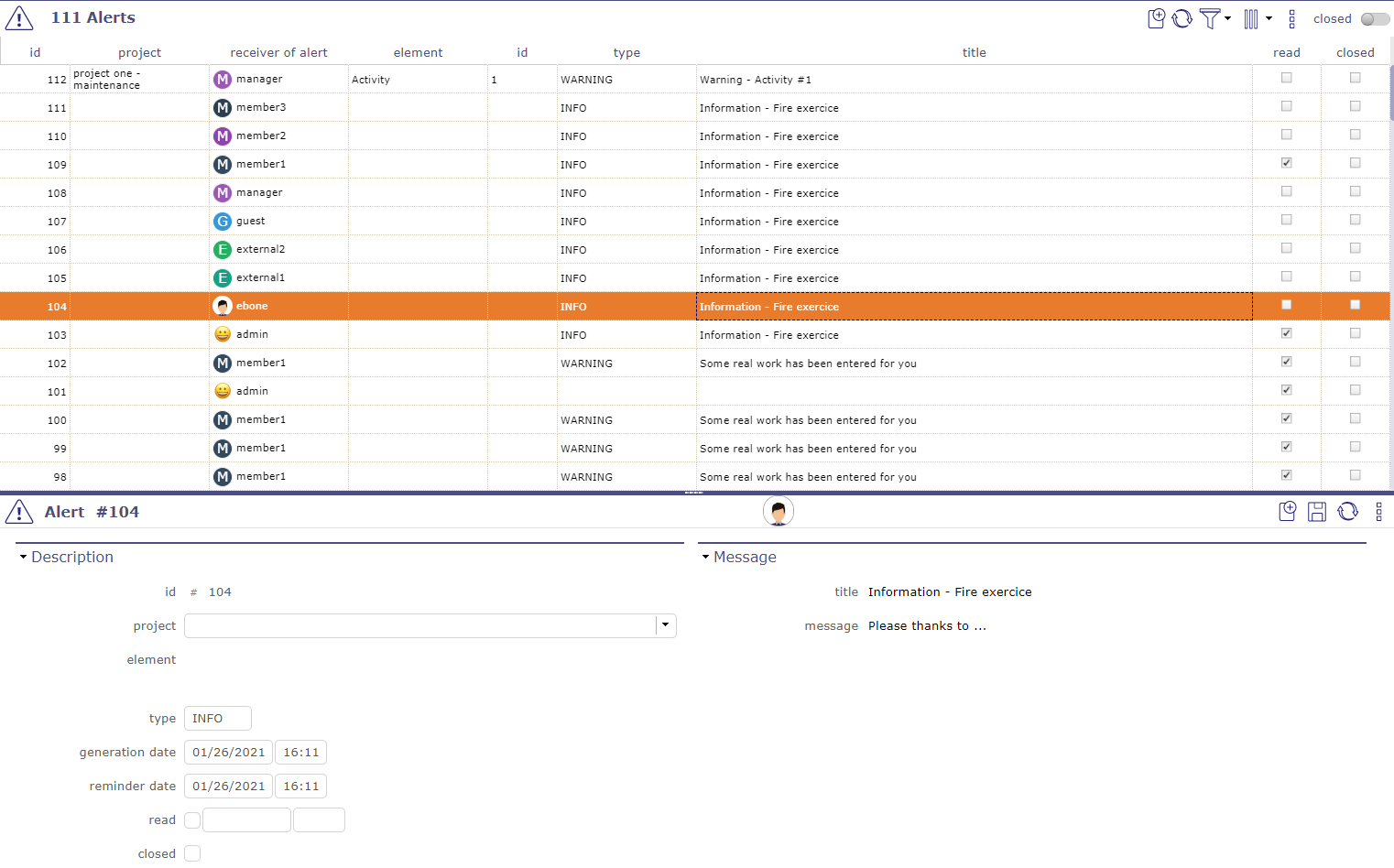
Alert screen¶
The button Mark as read is available ifxthe user alert is not tagged “read” yet.
Messages¶
You can define some message that will be displayed on the login and today screen.
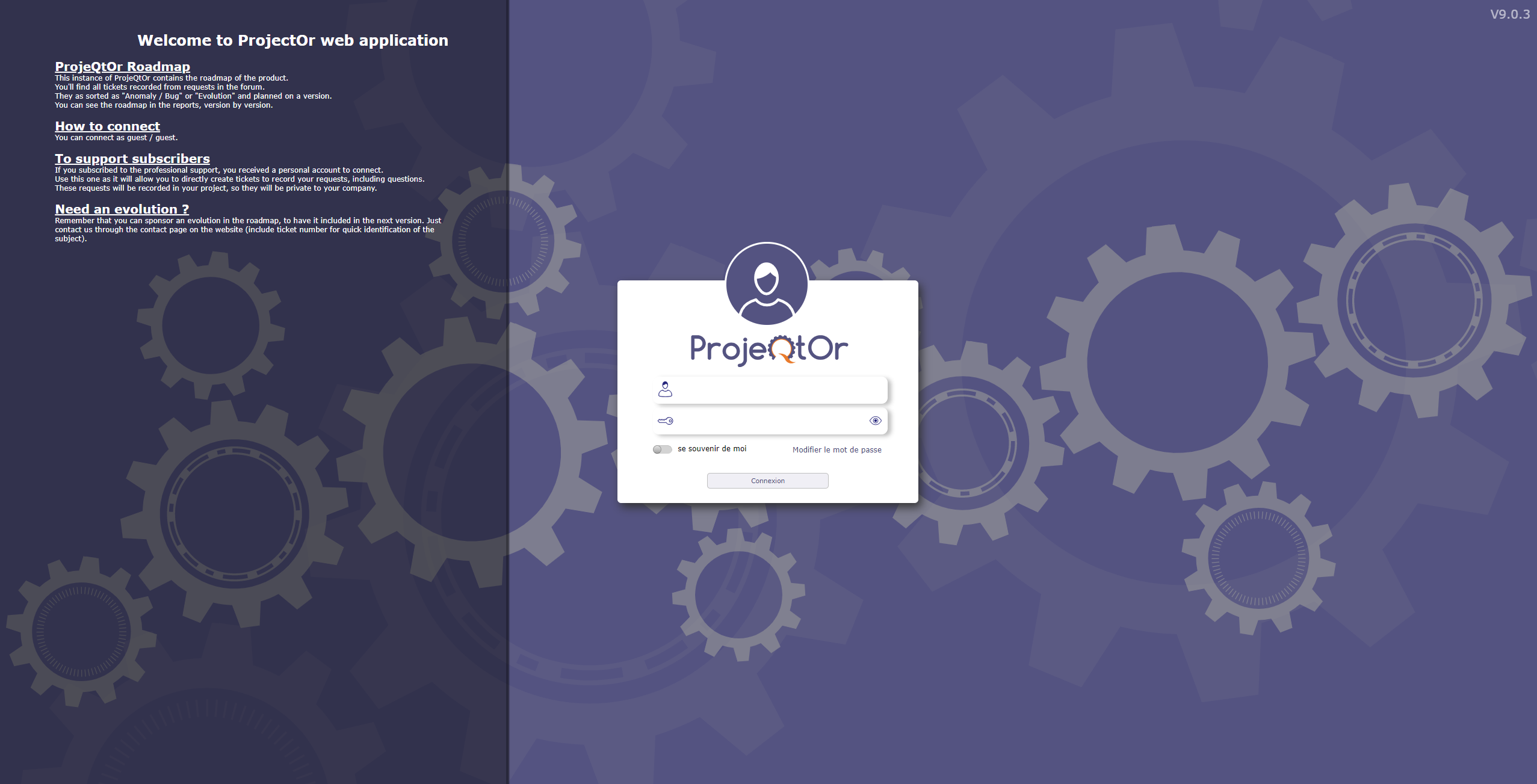
Login screen with message¶
Check the show on login screen box to see your message on the login screen.
Legal notice¶
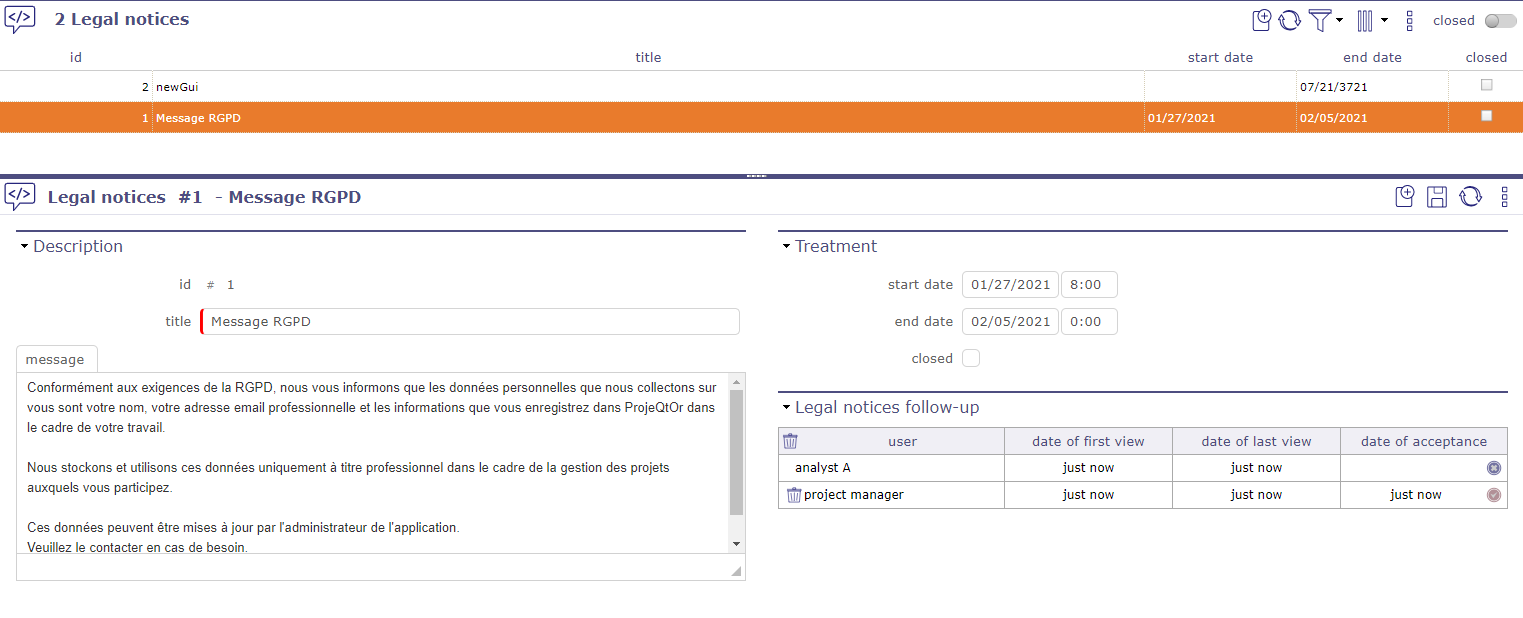
Legal notice screen¶
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) governs the processing of personal data in the territory of the European Union.
Above all, this involves informing people about what you do with their data and respecting their rights. As a data controller, or as a processor, you must take measures to ensure that this data is used that respects the privacy of the persons concerned.
You can define a “legal” message that will be displayed when you log in from the home screen.
For this message to disappear, it must be scrolled to the read confirmation button.
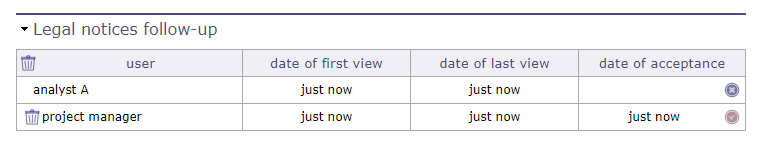
Legal notice screen¶
This allows you to have a real-time follow-up of the users who have confirmed the reading of this message.
Note
What is the GDPR?
The abbreviation GDPR stands for “General Data Protection Regulation” (GDPR). The GDPR governs the processing of personal data in the territory of the European Union.
The legal context adapts to follow developments in technologies and in our societies (increased use of digital technology, development of online commerce, etc.).
This new European regulation is a continuation of the French Data Protection Act of 1978 and strengthens the control by citizens of the use that may be made of data concerning them.
It harmonizes the rules in Europe by offering a unique legal framework to professionals. It helps to develop their digital activities in the EU based on the trust of users.
Visit the CNIL web site here
Import data¶
Imports data from CSV or XLSX files.
Select the element type from the list.
Select file format (CSV or XLSX).
Select the file.
Click on Import data button to start importing.
Report of the import
Data that is not imported because not recognized as a field appear in grey text in the result table.
Data that are voluntarily not imported (because must be calculated) appear in blue text in the result table.
Import users
The password field must be cut and pasted from the database because it is encrypted.
If you enter some readable password, the users will not be able to connect.
Warning
If you want to create new users don’t put any id because if id already exists, it will be overridden by the new (with possibility to erase admin user…).
Always keep in mind that your import may have some impact on administrator user.
So be sure to keep an operational admin access.
Importing document versions
Two ways to import document versions, by describing only the version with its standard fields and by describing the document and the version (the name of the fields of the version will be followed by ‘(DocumentVersion)’, or its translation into the current language).
The CSV import file may also include the importFile field that will give the link to the version.
The target field that can be set to delete, the file to be imported is deleted after import or a directory name. The file to be imported is moved to this directory after import) or nothing (the file to be imported is not modified).
File format¶
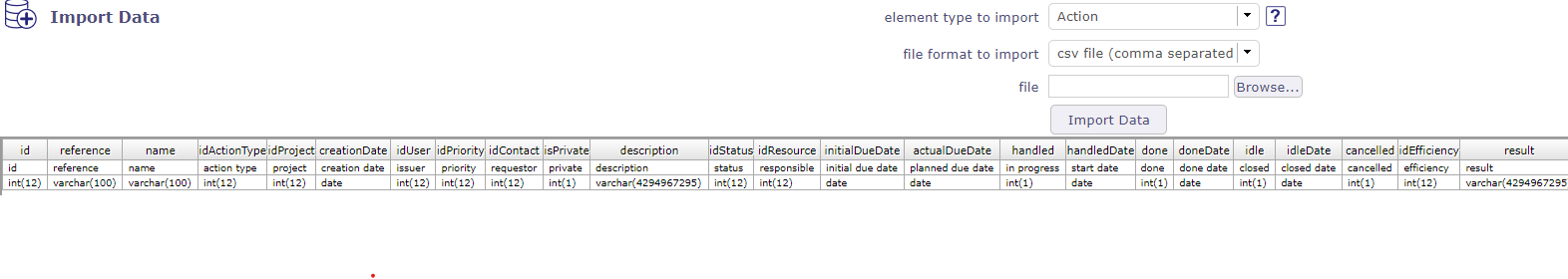
Import file format¶
The content of the imported file must fit the element type description.
To know the data that may be imported, click on the ![]() button.
button.
Names of columns
The first line of the file must contain the name of the fields.
Names of columns can contain spaces (to have better readability).
The spaces will be removed to get the name of the column.
Tip
Look into the model class. The names are the same.
Date format
Dates are expected in format “YYYY-MM-DD”.
Data import process¶
Operations are performed, depending on whether the element type, the column or the column value.
Column Id
You may add an “id” column in the file.
The import will try to update the corresponding element, and will fail if it does not exist.
The import will create a new element from the data.
Linked tables
For columns corresponding to linked tables (“idXxxx”), you can indicate as the column name either “idXxxx“ or “Xxxx” (without “id”) or the caption of the column (as displayed on screens).
If the value of the column is numeric, it is considered as the code of the item.
If the value of the column contains non numeric value, it is considered as the name of the item, and the code will be searched for the name.
In any case, columns with no data will not be updated. Then you can update only one field on an element.
To clear a data, enter the value “NULL” (not case sensitive).
Important
Do not import the value of “real work” on tickets, even if it is specified in the import file.
Automatic import¶
Imports can be automated. Files placed on a defined directory will automatically be imported.
Automatic import parameters must be set in Global parameters.
Background task must be started by Administration Console.
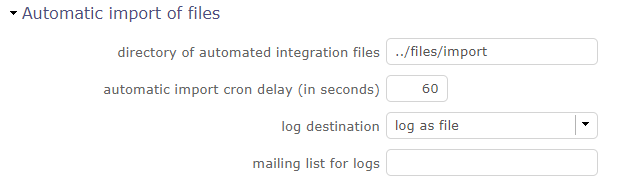
Automatic import files¶
The files must respect some basic rules.
File name format is: “Class”_”Timestamp”.”ext”: Example: Ticket_20241231_235959.csv)
Timestamp defined to be able to store several files in the directory.
Format is free. The recommended format is “YYYYMMDD_HHMMSS”.
File extension representing its format. Valid extensions are CSV and XLSX.
File format
The files must follow the ProjeQtOr File format and must be full and consistent.
Tip
The files should not be directly created in the import folder.
They must be created in a temporary folder and moved afterwards.
Import process
Correctly imported files are moved to a “done” sub folder of the import folder.
If an error occurs during import of a file, the full file is moved to “error” sub-folder of the import folder, even if there is only one error over many other items correctly integrated.
You can get the result as a log file and/or email summary.
Cloned Environnement¶
You can duplicate the complete environment (data and code) to form a simulation environment.
Important
The CRON program must be started and running so that the simulation request can be taken into account and can be generated.
The cloned Environment managment¶
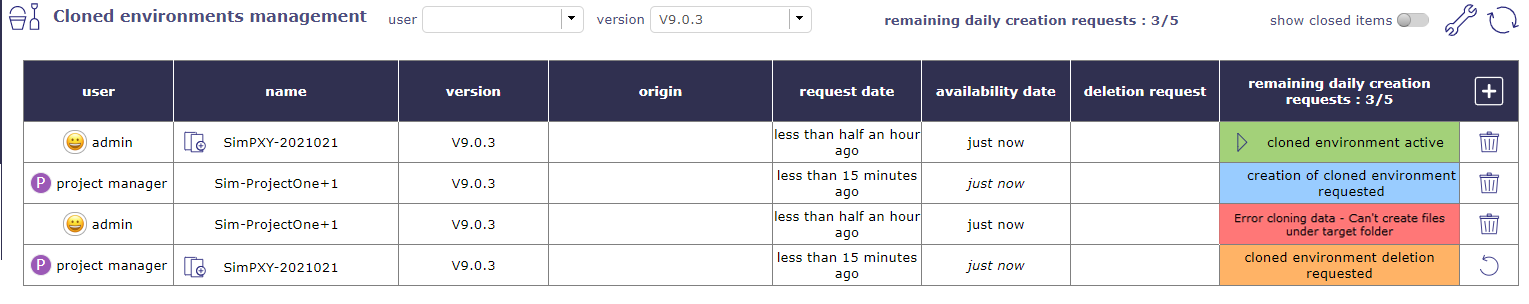
Cloned environment managment¶
This screen allows you to manage your queries for new simulation environments, to follow them or to request the deletion of a particular simulation.
You can also track requests from other users based on your profiles and your rights.
Click on ![]() to request the creation of a new simulation area, a pop up will appear allowing you to make your request.
to request the creation of a new simulation area, a pop up will appear allowing you to make your request.
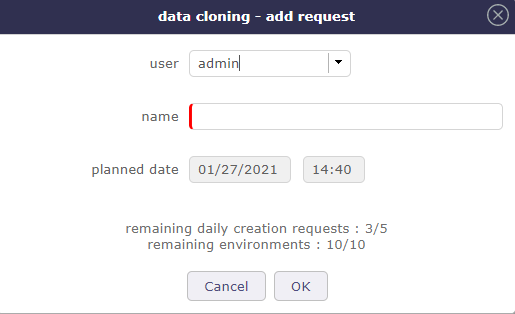
Add request¶
Identify the profile making the request, name your space and confirm your request by clicking on OK.
Note
The simulated databases will always have a name prefixed by simu_ followed by the name of the simulation.
Color code
Blue: Request being created
Orange: Warning (delete request)
Red: Error creating the environment (path, rights …)
Green: Environment creates
Go to the cloned Environment
When your simulation is ready, green status, you can open your cloned environment.
Click on ![]() to launch the environment.
to launch the environment.
A new tab opens with a new ProjeQtOr session. Authenticate yourself, you can start working in your environment.
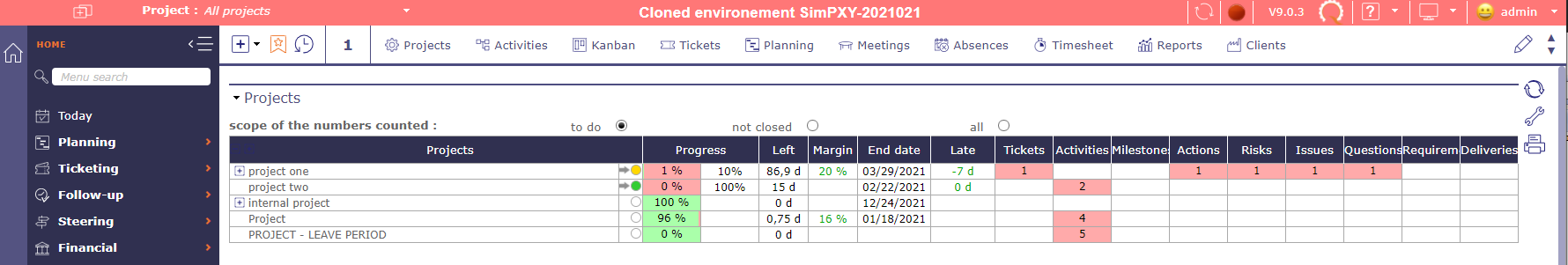
Cloned environment session¶
The instance area turns red when you are in a simulation space.
Not all screens or functions will be accessible in this space.
For example, you will not be able to request and create a new simulation space in your cloned environment.
Copy and delete a cloned Environment
You did a successful simulation on one of your cloned environment and you want the copy to run other tests but without touching the simulation.
Just copy this environment. The origin of the copy will then be indicated in the list with a shortcut to access it.
Deletion requests are stored in the simulation table. They are processed in the same process as creations, but always with priority to free up space before allocating new resources to new instances.
Tip
To avoid overly broad rights management and server invasion problems, all simulations (code) will be placed in a “simulation” directory outside of the main ProjeQtOr directory.
Thus, if the main instance is accessible via the url “projeqtor.xxx.fr”, the simulations will be accessible via the url “projeqtor.xxx.fr/simulation/nom_de_simulation”.
Administration of simulation requests¶
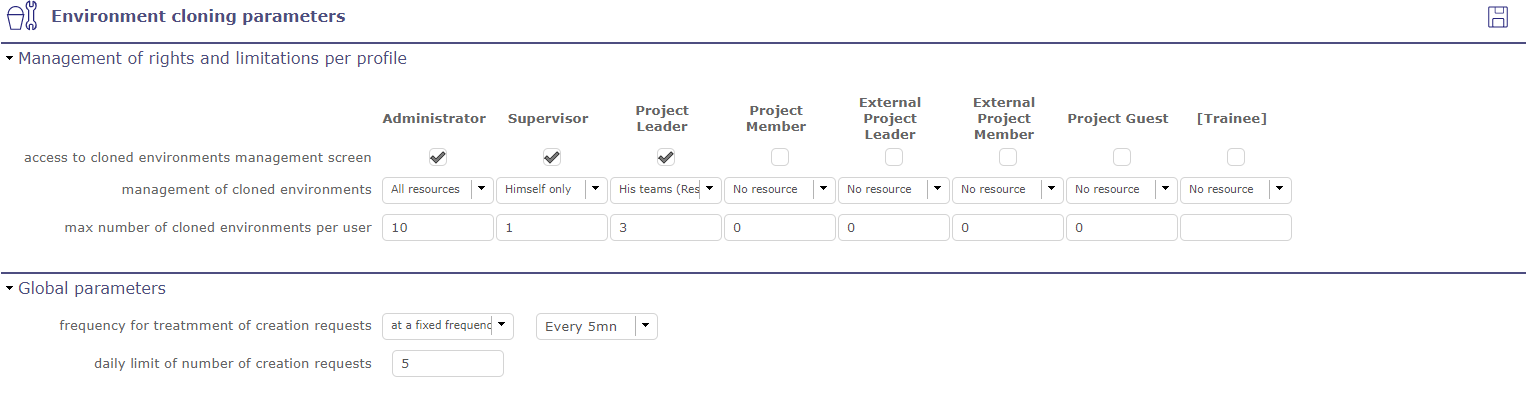
Cloned environment parameters¶
This parameters are also be accessible from simulated environments.
Click on ![]() on the Simulation management screen. You can limit the number of total simulations per profiles.
on the Simulation management screen. You can limit the number of total simulations per profiles.
This limitation can have some advantages:
Avoid saturating the server.
Force users to clean up their files.
Limit performance degradation caused by the creation of a simulated environment
The removal requests are decremented. If the limits are reached, the request screen to create a simulated environment is blocked.
Example of a invalid request due to too much creation request.¶
The time required to create a simulation space may vary. Depending on your database, your servers or even if several requests are generated simultaneously.
It is an operation which can take time. That is why you can set frequencies for creation requests.
Fixed frequency
Analyzes creation requests at regular intervals and starts the generation of simulation environment as soon as a request is encountered.
At a given time
In order to avoid any slowing down of the database, you can program the generations of the spaces at a specific time of the day. This allows these to be programmed outside working hours.
The creation of a simulation instance is a heavy process for the server: duplication of code, duplication of data. that’s why when generating your simulation space, not all data is copied. Lik archived data (closed), update history, attached documents and files, all automation email and notifications.
